-
Probably the most popular pattern form PHP and not only.
Motivation:
Restriction to a single instance of a resource across the app, accessible from anywhere.
Diagram:

Implementation:
The classic example for PHP is the database resource. The database connection must be unique across the app, not to establish multiple connections to the database and as a consequence resources to be wasted.
For a single instance to exist the constructor must only be accessible from a static method, and the resulting object must not have the posibillity to be cloned. Also the class must not be extensible.
Example:
1// db connection information 2define ( 'DB_HOST', 'localhost' ); 3define ( 'DB_USER', 'user' ); 4define ( 'DB_PASS', 'pass' ); 5define ( 'DB_DATABASE', 'db' ); 6 7/** 8 * Singleton class for database connection management using mysqli 9 */ 10final class SingletonDB { 11 12 /** 13 * Singleton instance 14 * 15 * @var SingletonDB 16 */ 17 protected static $_instance = null; 18 19 /** 20 * Connection resource 21 * 22 * @var resource 23 */ 24 protected $_connection = null; 25 26 /** 27 * Constructor which also connects to the database 28 * 29 */ 30 protected function __construct() { 31 // connection to database server 32 $this->_connection = new mysqli ( DB_HOST, DB_USER, DB_PASS ); 33 34 // in case of an error connection an exception is thrown 35 if ($this->_connection->connect_error) { 36 throw new Exception ( 'Error connection to mysql server' ); 37 } 38 39 // selecting the database 40 $this->_connection->select_db ( DB_DATABASE ); 41 42 // in case of an error selecting the database an exception is thrown 43 if ($this->_connection->error) { 44 throw new Exception ( 'Error selecting database' ); 45 } 46 47 } 48 49 /** 50 * Run SQL queries 51 * 52 * @param string $query SQL query 53 * @return mysqli_result 54 */ 55 public function query($query) { 56 return $this->_connection->query ( $query ); 57 } 58 59 /** 60 * Access for error messages 61 * 62 * @return string 63 */ 64 public function error() { 65 return $this->_connection->error; 66 } 67 68 /** 69 * Method that is called when cloning an object 70 * Is protected so is not possible to clone the object 71 * 72 */ 73 protected function __clone() { 74 } 75 76 /** 77 * Close connection and destroy the object 78 * 79 */ 80 public function __destruct() { 81 $this->_connection->close (); 82 } 83 84 /** 85 * Method that returns an SingletonDB instance 86 * 87 * @return SingletonDB 88 */ 89 public static function getInstance() { 90 if (self::$_instance == null) { 91 self::$_instance = new SingletonDB ( ); 92 } 93 94 return self::$_instance; 95 } 96} 97 98try { 99 // SingletonDB instance 100 $db = SingletonDB::getInstance (); 101 102 // Query to be run 103 $q = 'SELECT * FROM test'; 104 105 // the query will return an mysqli_result object 106 $result = $db->query ( $q ); 107 108 // check for errors and display them 109 if ($db->error ()) { 110 111 echo $db->error (); 112 113 } else { 114 // extract the result and display 115 while ( $row = $result->fetch_assoc () ) { 116 var_dump ( $row ); 117 } 118 // close mysqli_result object 119 $result->close (); 120 } 121// in case of exception there is displayed 122} catch ( Exception $e ) { 123 echo $e->getMessage (); 124} -
Iterator patter is probably the most popular pattern from SPL. Is a very simple way to demonstrate the advantages of an interface and SPL.
Motivation:
The possibility of iterating object type structures, using functions like foreach(), var_dump(), print_r() etc.Diagram:
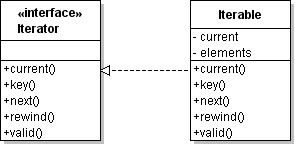
Iterator structure:
In SPL there are a lot of interfaces and classes for iteration.
Iterator interface base structure:
1/** 2 * Iterator interface from SPL 3 */ 4Iterator extends Traversable { 5 /** 6 * Returns the current element 7 */ 8 abstract public mixed current ( void ) 9 10 /** 11 * Returns the key of the current element 12 */ 13 abstract public scalar key ( void ) 14 15 /** 16 * Moves to the next element in the array 17 */ 18 abstract public void next ( void ) 19 20 /** 21 * Reset the iteration to the initial position 22 */ 23 abstract public void rewind ( void ) 24 25 /** 26 * Check to see if the current position is valid 27 */ 28 abstract public boolean valid ( void ) 29}Example 1:
A simple iterator object.
1/** 2 * The class for the iterator object 3 */ 4class Iterabil implements Iterator { 5 6 /** 7 * The index for the iterated element 8 */ 9 private $_current = 0; 10 11 /** 12 * Array with elements to iterate 13 */ 14 private $_elements = array(); 15 16 /** 17 * Constructor 18 * 19 * @param array $elements Elements to iterate 20 */ 21 public function __construct($elements) { 22 $this->_elements = $elements; 23 } 24 25 /** 26 * Current element 27 * 28 * @return mixed Current element 29 */ 30 public function current() { 31 return $this->_elements[$this->_current]; 32 } 33 34 /** 35 * Current index 36 * 37 * @return integer Current index 38 */ 39 public function key() { 40 return $this->_current; 41 } 42 43 /** 44 * Move to the next index 45 */ 46 public function next() { 47 $this->_current++; 48 } 49 50 /** 51 * Reset index 52 */ 53 public function rewind() { 54 $this->_current = 0; 55 } 56 57 /** 58 * Check if the current element is set 59 * 60 * @return boolean If the current element is set 61 */ 62 public function valid() { 63 return isset($this->_elements[$this->_current]); 64 } 65} 66 67// class instance 68$obj = new Iterabil(array(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)); 69 70// iterate object 71foreach ($obj as $value) { 72 echo $value.PHP_EOL; 73} 74 75// output: 76// 1 77// 2 78// 3 79// 4 80// 5Example 2:
Another example a little more complex, a class that allows to iterate through the public properties of a class which extends it. Iterator and Reflection are used.
1/** 2 * Class which iterates through the public properties of a class which extends it 3 */ 4class Iterabil implements Iterator { 5 6 /** 7 * The index for the iterated element 8 */ 9 private $_current = 0; 10 11 /** 12 * Array with elements to iterate 13 */ 14 private $_elements = array(); 15 16 /** 17 * Current element 18 * 19 * @return mixed Current element 20 */ 21 public function current() { 22 return $this->_elements[$this->_current]->name; 23 } 24 25 /** 26 * Current index 27 * 28 * @return integer Current index 29 */ 30 public function key() { 31 return $this->_current; 32 } 33 34 /** 35 * Move to next index 36 */ 37 public function next() { 38 $this->_current++; 39 } 40 41 /** 42 * Reset index and get the properties 43 */ 44 public function rewind() { 45 // rewind is the first to be called 46 // here the properties list should be obtained 47 // ReflectionClass is initialized 48 // with the current class name as a parameter 49 $reflection = new ReflectionClass(get_class($this)); 50 51 // we get the public properties 52 $this->_elements = $reflection->getProperties(ReflectionMethod::IS_PUBLIC); 53 54 // set the current index 55 $this->_current = 0; 56 } 57 58 /** 59 * Check if the current element is set 60 * 61 * @return boolean If the current element is set 62 */ 63 public function valid() { 64 return isset($this->_elements[$this->_current]); 65 } 66} 67 68/** 69 * A new class with public properties 70 * 71 */ 72class Testing extends Iterabil { 73 public $proprietate1; 74 public $proprietate2; 75} 76 77// class instance 78$obj = new Testing(); 79 80// iterate object 81foreach ($obj as $value) { 82 echo $value.PHP_EOL; 83} 84 85// output: 86// proprietate1 87// proprietate2And if you what the above example to be accessible as an array you just have to implement ArrayAccess from SPL.
ArrayAccess structure:
1ArrayAccess { 2 /** 3 * Check if the offset exists 4 */ 5 abstract public boolean offsetExists ( string $offset ); 6 7 /** 8 * Returns the element of an offset or NULL if it does not exist 9 */ 10 abstract public mixed offsetGet ( string $offset ); 11 12 /** 13 * Set a value for an offset 14 */ 15 abstract public void offsetSet ( string $offset , string $value ); 16 17 /** 18 * Unset a value for an offset 19 */ 20 abstract public void offsetUnset ( string $offset ) 21}Example 3:
An even more complicated example which shows the power of interfaces from SPL. Iterator object accessible like an array.
To simplify the array access logic I’ve used the php native functions for iterating an array (next(), reset()).
1/** 2 * The class for the iterator object 3 */ 4class Iterabil implements Iterator, ArrayAccess, Countable { 5 6 /** 7 * Array with elements to iterate 8 */ 9 private $_elements = array(); 10 11 /** 12 * Constructor 13 * 14 * @param array $elements Elementele de iterat 15 */ 16 public function __construct($elements) { 17 $this->_elements = $elements; 18 } 19 20 /** 21 * Current element 22 * 23 * @return mixed Current element 24 */ 25 public function current() { 26 return current($this->_elements); 27 } 28 29 /** 30 * Current index 31 * 32 * @return integer Current index 33 */ 34 public function key() { 35 return key($this->_elements); 36 } 37 38 /** 39 * Move to the next index 40 */ 41 public function next() { 42 next($this->_elements); 43 } 44 45 /** 46 * Reset index 47 */ 48 public function rewind() { 49 reset($this->_elements); 50 } 51 52 /** 53 * Check if the current element is set 54 * 55 * @return boolean If the current element is set 56 */ 57 public function valid() { 58 return current($this->_elements)?true:false; 59 } 60 /** 61 * Check if the offset exists 62 * 63 * @param string $offset Element key 64 * @return boolean If the element is set 65 */ 66 public function offsetExists($offset) { 67 return isset($this->_elements[$offset]); 68 } 69 70 /** 71 * Returns the element of an offset or NULL if it does not exist 72 * 73 * @param string $offset Array offset 74 * @return mixed Element or NULL 75 */ 76 public function offsetGet($offset) { 77 return $this->_elements[$offset]; 78 } 79 80 /** 81 * Set a value for an offset 82 * 83 * @param string $offset Element offset 84 * @param mixed $value Value of the element in the array 85 */ 86 public function offsetSet($offset, $value) { 87 $this->_elements[$offset] = $value; 88 } 89 90 /** 91 * Unset a value for an offset 92 * 93 * @param string $offset Element offset 94 */ 95 public function offsetUnset($offset) { 96 unset($this->_elements[$offset]); 97 } 98 99 /** 100 * Number of elements in the array 101 * 102 * @return integer Number of elements in array 103 */ 104 public function count() { 105 return count($this->_elements); 106 } 107} 108 109// Class instance 110$obj = new Iterabil(array(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)); 111 112echo 'Iteration using "for":'.PHP_EOL; 113 114// iterate the object like a simple array 115for($i = 0; $i < count($obj); $i++) { 116 echo $obj[$i].PHP_EOL; 117} 118 119echo 'Element to delete: '.$obj[1].PHP_EOL; 120 121unset($obj[1]); 122 123echo 'Iteration using "foreach":'.PHP_EOL; 124 125// iterate the object using foreach 126foreach ($obj as $element) { 127 echo $element.PHP_EOL; 128} 129 130// Output: 131//Iteration using "for": 132//1 133//2 134//3 135//4 136//5 137//Element to delete: 2 138//Iteration using "foreach": 139//1 140//3 141//4 142//5 -
Why there is so much talking about “bad code” or “bad practices”? Because they are important!
Lately I had an unpleasant experience with uncommented code, bad design, bad implemented oop, unoptimized and badly designed databases.Comments
Is a great mystery to me how it’s possible that every book and tutorial (not just PHP) to say that comments are not optional but MANDATORY and most often there entirely missing. Zend Studio has a very simple and efficient auto-complete system, you just have to tap “/**” and press enter, and then just complete the text. Netbeans has a similar system, just as easy.
And still, I’ve came over thousands of lines of code with almost no comments at all. The outcome? Hours and hours wasted trying to follow the logic!
Why is this happening? First reason: is boring, a developer want’s to write code not stories, usually seems like wasted time. The second reason: everything seems very logic when it’s written, if it’s so logic and fluent why waste time with stories? Because time passes, projects change, and with time is inevitable that the logic will be forgotten. Or another reason, new employees will come, in companies developers come and go, and the new guy can’t follow the logic with the same ease, in fact it is almost impossible to follow. Even the author of the code can’t follow the steps after a long period of time, sometimes the author was me.
In my opinion this should be a rule of thumb for every company, no class/method/property should be left uncommented. Time spend now on commentaries is time gain later when will be done debugging,optimization etc.
Bad design
I’ve encounter a question on an on-line “mini interview”: “do you see the importance of architect analysis before writing code?”, I’m sorry if the I didn’t get the exact question. The first time I’ve seen that question I had an “deja-vu” moment, a lot of the time I’ve started writing code only to realize that was the wrong approach.
A lot of the times, the issue is solved (apparently) with time and experience. Basically, if you get a beginner to write code, most likely he will have some bad approaches before getting a good one, and this is not abnormal, that’s why I think a beginner should be guided before he will begin to write code, and the resulting code to have a suggested logic by a “mentor”.
On the other extreme there are “software architects” which using UML they describe the logic and the structures using diagrams. When diagrams exist is much easier to follow the entire process and structure of the app. An experienced architect will be able to see the possible issues that may appear before beginning to write code, and when code is starting to be written everyone knows just what they have to do.
OOP is probably the most affected by poor design. Lately I’ve seen a lot of classes which had no internal structure, there ware just simple wrappers for SQL queries. That’s not OOP!
OOP is about abstracting elements in classes and objects. For instance the keyboard is a class which has keys (a child class) with various properties (letters, key code, position), some LEDs (another child class) etc. The way there organize in the database is not necessary in a tight relation with the resulting objects, as it may seem.
If your using OOP and what you are reading now sounds weird, try drawing on a piece of paper a diagram of the objects in your app and the references between them. If you can’t, it means that your approach to the OOP is wrong (or you just don’t know to draw a diagram 🙂 )!
We all make mistakes when it comes to OOP, but that’s not an excuse not to correct them, and to try to make architecture before code.
A bad app design may have very important financial implications. Time is money, and if an app has poor design, is not correctly structured, the debugging time is big, changes and enhancements require a lot of time, is a lot of code redundancy, etc. , then you can be sure your losing money.
A tool that I sometimes use is Violet UML Editor, is not a true UML editor like Rational Rose for instance, but rather an open-source toy. With Violet you can only build visual diagrams, but they can be useful to visually structure an app.
Databases
Why are PHP developers avoiding to truly learn MySQL? Sounds strange? Is very true though. Modifying PHP code is usually not very difficult (I mean the practical rewriting the code), but a bad database design is most of the times more difficult to change because is the risk of losing data.
A few weeks ago I’ve made a diagram of the database using MySQL Dump and MySQL Workbench. I was quite surprise to see tables which didn’t have relation keys with the tables from which the information came from (I don’t mean settings tables or other tables which logically don’t have a relation with the other tables), then the data source was completely lost.
Another classic problem with beginners is that when they have a relation table between two other tables, like categories and products for instance, the primary key is on a field like “id” which has no relevance. A primary key can be set on multiple fields, like for the previous example “id_category, id_product” not “id”, this way you ensure the uniqueness of a product in a category using the primary key restriction.
Another thing that is usually avoided are the indexes. In a previous blog post I was shortly explaining them, insufficient even though there important. An index can significantly reduce the search time in a table, from tenths of a second to a thousandths of a second. A badly optimized app from this point of view can have a significant bigger response time then normal.
Frameworks
To quote a classical phrase in the PHP community:
and Laura Thomson had some strong reasons to back this up.
Somebody was saying last week that the reason for bad code is actually PHP and it’s loose typing. Let’s be honest, if we take in consideration a language like C++ there are a lot more issues that can arise. I remember in faculty how bad my C++ code was, and the problem wasn’t the language but rather my skills at that time. PHP allows approaches from OOP to spaghetti code (OOP, procedural, closures, labels). The fact that many developers chose bad approaches is not a language problem, there is the same approach issue with a language like C++, or in fact with any programming language out there.
Why are less design problems in Ruby on Rails for instance? Because is a framework! I’ve never heard of anybody doing web developing just using Ruby (there are developers out there, especially for desktop apps, but that’s another story), of course there are less issues when using a framework. The same way PHP issues can be reduced using an popular framework.
There are tens or even hundreds of open-source PHP frameworks. Of this there are a few really popular, like Zend Framework, CakePHP, Symfony, Solar, CodeIgniter etc. An great advantage when using a popular framework is that is easy to find professionals. Another big advantage is that you have a well tested and documented code base, thing that is very hard to achieve in a small company.
Or even if your using an in-house framework I thing is a good idea to adopt a structure of an popular framework to reduce the learning curve for new developers.
Using an popular open-source framework usually you reduce the working time and the time to develop nu features because usually there included in the framework, so economical advantages bay arise (money), a better structure and last but not least happier developers (which I’m not at this time).
Concluding:
- set some rules for the code standards, don’t forget to add the comments to the list,
- make sure the app design is according to a plan that allows for scalability and minimal code redundancy,
- make sure the database is well structured and optimized,
- consider an open-source popular framework over building an internal one.
Using this simple rules will save resources, time, and probably developers will be more happy with there result.
-
Today I’ve updated the romanian stemmer class to version 0.6.
It used to display notices, but now there are corrected.
Enjoy!
-
One of the biggest issues with the web is encoding.
In the old days the formerly base standard was ISO 8859-1, where there ware 191 latin characters defined, and 1 char = 1B. For different languages, different encodings ware used, but from here many portability issues appeared, the possibility to cover a greater number of languages etc.
The problem occurs when a project should be available in several languages, and the number of the languages is not controlled. A big project like WordPress for example should be available with any language.
Unicode is a better alternative for ISO 8859-1, having more then 100.000 characters defined. In other words it has about every character of about any existing language.
As I was saying for MySQL, UTF-8 characters have a variable length between 1 and 4B.
Displaying the UTF-8 content in PHP pages
For browser to interpret the page content as UTF-8, it should receive the right headers:
1<?php header("Content-type: text/html; charset=utf-8");?>Attention! The header should be the first thing that is send from the server! In other words it should be the first thing displayed on the page.
The type of the document can be specified with the “Content-Type” meta tag. If there is a similar meta tag on the page it should be removed and replace with:
1<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8">The .htaccess file and string processing
Add to the .htaccess file (for Apache servers) the following lines:
1# default charset used by PHP 2php_value default_charset utf-8 3# encoding for mbstring 4php_value mbstring.internal_encoding utf-8 5php_value mbstring.func_overload 7The first line sets the default charset for PHP, this setting can be made directly to php.ini.
Second and third line sets the mbstring (multi byte string) functions.
Using UTF-8, as I was saying earlier, 1 char != 1B, so errors may appear:
1$var = 'aşadar'; 2 3echo strlen($var).PHP_EOL; // 7 4echo strtoupper($var).PHP_EOL; // AşADAR 5 6// using mbstring functions 7echo mb_strlen($var).PHP_EOL; // 6 8echo mb_strtoupper($var).PHP_EOL; // AŞADARThis is why we set the mbstring functions mode using the .htaccess file. Content entered through forms should be processed using mbstring functions, to avoid problems like in the earlier example.
The available functions are in the manual.
Coding old content
There are many ways to encode ISO 8859-1 content to UTF-8. A couple of ways of doing that with PHP are:
– iconv() function which converts from a format to another specified format:
1echo iconv("ISO-8859-1", "UTF-8", "Test");– utf8_encode() function which converts from ISO 8859-1 to UTF-8:
1echo utf8_encode("Test");What does the future bring?
The long-expected PHP6 will have native support for Unicode, so all the above tricks will be unnecessary. At the moment of writing this blog PHP 6 is 70.70% done, and with a little luck it will be ready in less then an year.