-
Factory method design pattern introduced by GoF (Gang of Four) which I’ve talked about in a previous blog, has the base idea of a method that generates objects. Most implementations are “poor”, because they use a lot of hard-coding for the factory (just like me in the previous blog).
PHP 5.3 offers the possibility of a very interesting implementation using “Late static bindings“.
The classes from which the objects will be generated are:
1// abstract base class that will be inherited 2abstract class Drink { 3 4 // ingredients 5 protected $ingredients; 6 7 // public method for producing the drink 8 abstract public function MakeDrink(); 9} 10 11// a child class for tea 12class Tea_Drink extends Drink { 13 14 // ingredients for tea 15 protected $ingredients = array('tea', 'sugar', 'mink', 'water'); 16 17 // make tea 18 public function MakeDrink() { 19 20 // make tea 21 } 22} 23 24// another class for Bloody Mary 25class BloodyMary_Drink extends Drink { 26 27 // ingredients for Bloody Mary 28 protected $ingredients = array('votka', 'salt', 'tomato juice'); 29 30 // make Bloody Mary 31 public function MakeDrink() { 32 33 // make BloodyMary 34 35 } 36}The idea is to have an abstract factory class to extend as simple as possible when creating each new factory class.
PHP 5
In PHP 5 the class will look something like this:
1// abstract Factory class 2abstract class absFactory { 3 4 // name of the base class 5 static protected $base_class = ''; 6 7 // factory method 8 public static function getInstance($type) { 9 10 // name of the resulting class 11 $class_name = $type . '_' . self::$base_class; 12 13 // check if class exists 14 // here you can add an autoloader 15 if(!class_exists($class_name)) { 16 throw new Exception( 'Class ' . $class_name . ' not loaded!'); 17 } 18 19 // check to see if the class inherits the base class 20 if(!is_subclass_of($class_name, self::$base_class)) { 21 throw new Exception( 22 'Class ' . $class_name . ' is not a child of ' . self::$base_class 23 ); 24 } 25 26 // new object 27 return new $class_name; 28 29 } 30 31}Because the getInstance() method is static the property will be static too.
If we try:
1class DrinkFactory extends absFactory { 2 3 static protected $base_class = 'Drink'; 4} 5 6try { 7 8 $obj = DrinkFactory::getInstance('Tea'); 9 10} catch (Exception $e) { 11 12 echo $e->getMessage(); 13}The output will be:
1Class Tea_ not loaded!Because of the “self”, we can’t just call the method using the child class because the value of $base_class will be “” and not “Drink”, we must overwrite the getInstance() method. Which is quite “complicated”.
A working version in PHP 5 will be:
1class DrinkFactory extends absFactory { 2 3 public static function getInstance($type) { 4 5 self::$base_class = 'Drink'; 6 7 // factory method of the base factory class 8 parent::getInstance($type); 9 10 } 11 12} 13 14try { 15 16 $obj = DrinkFactory::getInstance('Tea'); 17 18} catch (Exception $e) { 19 20 echo $e->getMessage(); 21}But is not exactly “elegant”.
PHP 5.3
Here we have “Late static bindings”, which is basically introducing the work “static”.
The base factory class will look something like this:
1// abstract Factory class 2abstract class absFactory { 3 4 // name of the base class 5 static protected $base_class = ''; 6 7 // factory method 8 public static function getInstance($type) { 9 10 // name of the resulting class 11 $class_name = $type . '_' . static::$base_class; 12 13 // check if class exists 14 // here you can add an autoloader 15 if(!class_exists($class_name)) { 16 throw new Exception( 'Class ' . $class_name . ' not loaded!'); 17 } 18 19 // check to see if the class inherits the base class 20 if(!is_subclass_of($class_name, static::$base_class)) { 21 throw new Exception( 22 'Class ' . $class_name . ' is not a child of ' . static::$base_class 23 ); 24 } 25 26 // new object 27 return new $class_name; 28 29 } 30 31}A change so small allows us to create a much “nicer” factory class:
1class DrinkFactory extends absFactory { 2 3 static protected $base_class = 'Drink'; 4 5} 6 7try { 8 9 $obj = DrinkFactory::getInstance('Tea'); 10 11} catch (Exception $e) { 12 13 echo $e->getMessage(); 14}Basically in this version only the relevant property in this context is overwritten.
-
An creational design pattern, which represents an solution for generation objects without specifying the class name. Virtually all methods that generate objects are particular implementations of the Factory Method pattern.
Motivation:
A motivation for this choice is that the creation of the object is delegated to the factory method.
Diagram:
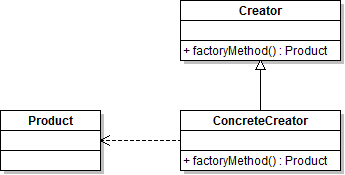
Implementation:
The classes that generates the objects, the common class to extend and the class with the factory method:1// the common class to be extended 2abstract class OutputBase { 3 // output the necessary headers 4 abstract public function header(); 5 6 // resulting body 7 abstract public function body($data); 8 9} 10 11// class for XML ouput 12class XMLOutput extends OutputBase { 13 14 // output XML header 15 public function header() { 16 header('content-type: text/xml'); 17 } 18 19 // xml document 20 public function body($data) { 21 $res = ''; 22 23 $res .= ''; 24 25 foreach ($data as $root => $item) { 26 27 $res .= ''; 28 29 foreach ($item as $key => $val) { 30 $res .= '<'.$key.'>'.$val.''; 31 } 32 33 $res .= ''; 34 } 35 36 $res .= ''; 37 38 return $res; 39 40 } 41 42} 43 44// class for CSV output 45class CSVOutput extends OutputBase { 46 47 // output CSV header 48 public function header() { 49 header("Content-type: text/plain"); 50 } 51 52 // CSV body 53 public function body($data) { 54 $res = ''; 55 56 $keys = array_keys($data[0]); 57 58 foreach ($keys as $key) { 59 $res .= '"'.$key.'";'; 60 } 61 $res .= "\r\n"; 62 63 foreach ($data as $item) { 64 foreach ($item as $val) { 65 $res .= '"'.$val.'";'; 66 } 67 68 $res .= "\r\n"; 69 } 70 71 return $res; 72 } 73} 74 75// the factory method class 76// is abstract so it wont be instantiated 77abstract class OutputFactory { 78 79 // constant for XML type 80 const XML = 1; 81 82 // constant for CSV type 83 const CSV = 2; 84 85 // static factory method 86 public static function getInstance($type) { 87 // depending which constant was received as a parameter 88 // one of the objects will be returned 89 switch ($type) { 90 case self::XML : 91 return new XMLOutput(); 92 break; 93 94 case self::CSV : 95 return new CSVOutput(); 96 break; 97 } 98 99 // if the value received as a parameter is not one of the constants 100 // an exception will be thrown 101 throw new Exception('Invalid class type!'); 102 } 103 104}Example:
1// the data 2$data = array( 3 array( 4 'a' => 1, 5 'b' => 2, 6 'c' => 3 7 ), 8 array( 9 'a' => 4, 10 'b' => 5, 11 'c' => 6 12 ) 13 ); 14 15// try-catch block in case of an exception 16try { 17 // generation the object 18 $obj = OutputFactory::getInstance(OutputFactory::XML); 19 20 // output headers 21 $obj->header(); 22 23 // display body 24 echo $obj->body($data); 25 26} catch (Exception $e) { 27 28 $e->getMessage(); 29 30} -
Probably the most popular pattern form PHP and not only.
Motivation:
Restriction to a single instance of a resource across the app, accessible from anywhere.
Diagram:

Implementation:
The classic example for PHP is the database resource. The database connection must be unique across the app, not to establish multiple connections to the database and as a consequence resources to be wasted.
For a single instance to exist the constructor must only be accessible from a static method, and the resulting object must not have the posibillity to be cloned. Also the class must not be extensible.
Example:
1// db connection information 2define ( 'DB_HOST', 'localhost' ); 3define ( 'DB_USER', 'user' ); 4define ( 'DB_PASS', 'pass' ); 5define ( 'DB_DATABASE', 'db' ); 6 7/** 8 * Singleton class for database connection management using mysqli 9 */ 10final class SingletonDB { 11 12 /** 13 * Singleton instance 14 * 15 * @var SingletonDB 16 */ 17 protected static $_instance = null; 18 19 /** 20 * Connection resource 21 * 22 * @var resource 23 */ 24 protected $_connection = null; 25 26 /** 27 * Constructor which also connects to the database 28 * 29 */ 30 protected function __construct() { 31 // connection to database server 32 $this->_connection = new mysqli ( DB_HOST, DB_USER, DB_PASS ); 33 34 // in case of an error connection an exception is thrown 35 if ($this->_connection->connect_error) { 36 throw new Exception ( 'Error connection to mysql server' ); 37 } 38 39 // selecting the database 40 $this->_connection->select_db ( DB_DATABASE ); 41 42 // in case of an error selecting the database an exception is thrown 43 if ($this->_connection->error) { 44 throw new Exception ( 'Error selecting database' ); 45 } 46 47 } 48 49 /** 50 * Run SQL queries 51 * 52 * @param string $query SQL query 53 * @return mysqli_result 54 */ 55 public function query($query) { 56 return $this->_connection->query ( $query ); 57 } 58 59 /** 60 * Access for error messages 61 * 62 * @return string 63 */ 64 public function error() { 65 return $this->_connection->error; 66 } 67 68 /** 69 * Method that is called when cloning an object 70 * Is protected so is not possible to clone the object 71 * 72 */ 73 protected function __clone() { 74 } 75 76 /** 77 * Close connection and destroy the object 78 * 79 */ 80 public function __destruct() { 81 $this->_connection->close (); 82 } 83 84 /** 85 * Method that returns an SingletonDB instance 86 * 87 * @return SingletonDB 88 */ 89 public static function getInstance() { 90 if (self::$_instance == null) { 91 self::$_instance = new SingletonDB ( ); 92 } 93 94 return self::$_instance; 95 } 96} 97 98try { 99 // SingletonDB instance 100 $db = SingletonDB::getInstance (); 101 102 // Query to be run 103 $q = 'SELECT * FROM test'; 104 105 // the query will return an mysqli_result object 106 $result = $db->query ( $q ); 107 108 // check for errors and display them 109 if ($db->error ()) { 110 111 echo $db->error (); 112 113 } else { 114 // extract the result and display 115 while ( $row = $result->fetch_assoc () ) { 116 var_dump ( $row ); 117 } 118 // close mysqli_result object 119 $result->close (); 120 } 121// in case of exception there is displayed 122} catch ( Exception $e ) { 123 echo $e->getMessage (); 124} -
Iterator patter is probably the most popular pattern from SPL. Is a very simple way to demonstrate the advantages of an interface and SPL.
Motivation:
The possibility of iterating object type structures, using functions like foreach(), var_dump(), print_r() etc.Diagram:
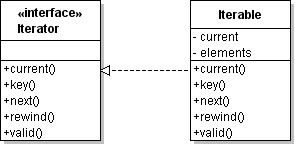
Iterator structure:
In SPL there are a lot of interfaces and classes for iteration.
Iterator interface base structure:
1/** 2 * Iterator interface from SPL 3 */ 4Iterator extends Traversable { 5 /** 6 * Returns the current element 7 */ 8 abstract public mixed current ( void ) 9 10 /** 11 * Returns the key of the current element 12 */ 13 abstract public scalar key ( void ) 14 15 /** 16 * Moves to the next element in the array 17 */ 18 abstract public void next ( void ) 19 20 /** 21 * Reset the iteration to the initial position 22 */ 23 abstract public void rewind ( void ) 24 25 /** 26 * Check to see if the current position is valid 27 */ 28 abstract public boolean valid ( void ) 29}Example 1:
A simple iterator object.
1/** 2 * The class for the iterator object 3 */ 4class Iterabil implements Iterator { 5 6 /** 7 * The index for the iterated element 8 */ 9 private $_current = 0; 10 11 /** 12 * Array with elements to iterate 13 */ 14 private $_elements = array(); 15 16 /** 17 * Constructor 18 * 19 * @param array $elements Elements to iterate 20 */ 21 public function __construct($elements) { 22 $this->_elements = $elements; 23 } 24 25 /** 26 * Current element 27 * 28 * @return mixed Current element 29 */ 30 public function current() { 31 return $this->_elements[$this->_current]; 32 } 33 34 /** 35 * Current index 36 * 37 * @return integer Current index 38 */ 39 public function key() { 40 return $this->_current; 41 } 42 43 /** 44 * Move to the next index 45 */ 46 public function next() { 47 $this->_current++; 48 } 49 50 /** 51 * Reset index 52 */ 53 public function rewind() { 54 $this->_current = 0; 55 } 56 57 /** 58 * Check if the current element is set 59 * 60 * @return boolean If the current element is set 61 */ 62 public function valid() { 63 return isset($this->_elements[$this->_current]); 64 } 65} 66 67// class instance 68$obj = new Iterabil(array(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)); 69 70// iterate object 71foreach ($obj as $value) { 72 echo $value.PHP_EOL; 73} 74 75// output: 76// 1 77// 2 78// 3 79// 4 80// 5Example 2:
Another example a little more complex, a class that allows to iterate through the public properties of a class which extends it. Iterator and Reflection are used.
1/** 2 * Class which iterates through the public properties of a class which extends it 3 */ 4class Iterabil implements Iterator { 5 6 /** 7 * The index for the iterated element 8 */ 9 private $_current = 0; 10 11 /** 12 * Array with elements to iterate 13 */ 14 private $_elements = array(); 15 16 /** 17 * Current element 18 * 19 * @return mixed Current element 20 */ 21 public function current() { 22 return $this->_elements[$this->_current]->name; 23 } 24 25 /** 26 * Current index 27 * 28 * @return integer Current index 29 */ 30 public function key() { 31 return $this->_current; 32 } 33 34 /** 35 * Move to next index 36 */ 37 public function next() { 38 $this->_current++; 39 } 40 41 /** 42 * Reset index and get the properties 43 */ 44 public function rewind() { 45 // rewind is the first to be called 46 // here the properties list should be obtained 47 // ReflectionClass is initialized 48 // with the current class name as a parameter 49 $reflection = new ReflectionClass(get_class($this)); 50 51 // we get the public properties 52 $this->_elements = $reflection->getProperties(ReflectionMethod::IS_PUBLIC); 53 54 // set the current index 55 $this->_current = 0; 56 } 57 58 /** 59 * Check if the current element is set 60 * 61 * @return boolean If the current element is set 62 */ 63 public function valid() { 64 return isset($this->_elements[$this->_current]); 65 } 66} 67 68/** 69 * A new class with public properties 70 * 71 */ 72class Testing extends Iterabil { 73 public $proprietate1; 74 public $proprietate2; 75} 76 77// class instance 78$obj = new Testing(); 79 80// iterate object 81foreach ($obj as $value) { 82 echo $value.PHP_EOL; 83} 84 85// output: 86// proprietate1 87// proprietate2And if you what the above example to be accessible as an array you just have to implement ArrayAccess from SPL.
ArrayAccess structure:
1ArrayAccess { 2 /** 3 * Check if the offset exists 4 */ 5 abstract public boolean offsetExists ( string $offset ); 6 7 /** 8 * Returns the element of an offset or NULL if it does not exist 9 */ 10 abstract public mixed offsetGet ( string $offset ); 11 12 /** 13 * Set a value for an offset 14 */ 15 abstract public void offsetSet ( string $offset , string $value ); 16 17 /** 18 * Unset a value for an offset 19 */ 20 abstract public void offsetUnset ( string $offset ) 21}Example 3:
An even more complicated example which shows the power of interfaces from SPL. Iterator object accessible like an array.
To simplify the array access logic I’ve used the php native functions for iterating an array (next(), reset()).
1/** 2 * The class for the iterator object 3 */ 4class Iterabil implements Iterator, ArrayAccess, Countable { 5 6 /** 7 * Array with elements to iterate 8 */ 9 private $_elements = array(); 10 11 /** 12 * Constructor 13 * 14 * @param array $elements Elementele de iterat 15 */ 16 public function __construct($elements) { 17 $this->_elements = $elements; 18 } 19 20 /** 21 * Current element 22 * 23 * @return mixed Current element 24 */ 25 public function current() { 26 return current($this->_elements); 27 } 28 29 /** 30 * Current index 31 * 32 * @return integer Current index 33 */ 34 public function key() { 35 return key($this->_elements); 36 } 37 38 /** 39 * Move to the next index 40 */ 41 public function next() { 42 next($this->_elements); 43 } 44 45 /** 46 * Reset index 47 */ 48 public function rewind() { 49 reset($this->_elements); 50 } 51 52 /** 53 * Check if the current element is set 54 * 55 * @return boolean If the current element is set 56 */ 57 public function valid() { 58 return current($this->_elements)?true:false; 59 } 60 /** 61 * Check if the offset exists 62 * 63 * @param string $offset Element key 64 * @return boolean If the element is set 65 */ 66 public function offsetExists($offset) { 67 return isset($this->_elements[$offset]); 68 } 69 70 /** 71 * Returns the element of an offset or NULL if it does not exist 72 * 73 * @param string $offset Array offset 74 * @return mixed Element or NULL 75 */ 76 public function offsetGet($offset) { 77 return $this->_elements[$offset]; 78 } 79 80 /** 81 * Set a value for an offset 82 * 83 * @param string $offset Element offset 84 * @param mixed $value Value of the element in the array 85 */ 86 public function offsetSet($offset, $value) { 87 $this->_elements[$offset] = $value; 88 } 89 90 /** 91 * Unset a value for an offset 92 * 93 * @param string $offset Element offset 94 */ 95 public function offsetUnset($offset) { 96 unset($this->_elements[$offset]); 97 } 98 99 /** 100 * Number of elements in the array 101 * 102 * @return integer Number of elements in array 103 */ 104 public function count() { 105 return count($this->_elements); 106 } 107} 108 109// Class instance 110$obj = new Iterabil(array(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)); 111 112echo 'Iteration using "for":'.PHP_EOL; 113 114// iterate the object like a simple array 115for($i = 0; $i < count($obj); $i++) { 116 echo $obj[$i].PHP_EOL; 117} 118 119echo 'Element to delete: '.$obj[1].PHP_EOL; 120 121unset($obj[1]); 122 123echo 'Iteration using "foreach":'.PHP_EOL; 124 125// iterate the object using foreach 126foreach ($obj as $element) { 127 echo $element.PHP_EOL; 128} 129 130// Output: 131//Iteration using "for": 132//1 133//2 134//3 135//4 136//5 137//Element to delete: 2 138//Iteration using "foreach": 139//1 140//3 141//4 142//5 -
Observer pattern refers to a class called “subject” that has a list of dependents, called observers, and notifies them automatically each time an action is taking place.
A small example of why is used:
– let’s say we have a class with does someting:
1class Actiune { 2 private $val; 3 function __construrct() { 4 // someting in the constructor 5 } 6 7 function change($val) { 8 $this->val = $val; 9 } 10}Each time $val changes we want to call a method of an “observer” object:
1class Actiune { 2 private $val; 3 function __construrct() { 4 // someting in the constructor 5 } 6 7 function change($val, $observator) { 8 $this->val = $val; 9 $observator->update($this); 10 } 11}Theoretically is not bad, but the more methods there are so does the dependence grows bigger and each time we add a new observer object we must modify the class, with will probably result in chaos, which will be almost impossible to port.
Now, the observator pattern looks something like this:
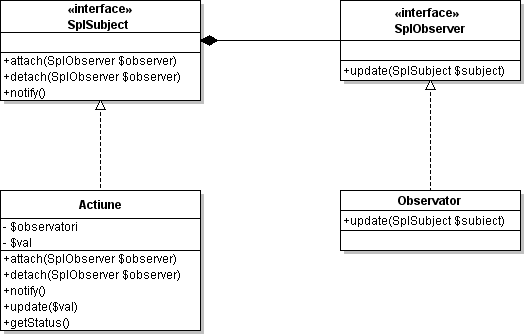
SPL (Standard PHP Library), which is well known for it’s defined iterators, comes with the interfaces SplSubject and SplObserver, for the subject and respectively the observer.
An implementation looks someting like this:
1/** 2 * the class which must be monitored 3 */ 4class Actiune implements SplSubject { 5 private $observatori = array(); 6 private $val; 7 8 /** 9 * method to attach an observer 10 * 11 * @param SplObserver $observator 12 */ 13 function attach(SplObserver $observator) { 14 $this->observatori[] = $observator; 15 } 16 17 /** 18 * method to detach an observer 19 * 20 * @param SplObserver $observator 21 */ 22 function detach(SplObserver $observator) { 23 $observatori = array(); 24 foreach($this->observatori as $observatorul) { 25 if($observatorul != $observator) $observatori[] = $observatorul; 26 } 27 $this->observatori = $observatori; 28 } 29 30 /** 31 * method that notifies the observer objects 32 */ 33 function notify() { 34 foreach($this->observatori as $observator) { 35 $observator->update($this); 36 } 37 } 38 39 /** 40 * method for makeing changes in the class 41 * 42 * @param int $val 43 */ 44 function update($val) { 45 echo 'updateing...'; 46 $this->val = $val; 47 $this->notify(); 48 } 49 50 /** 51 * public method with the subject's status 52 * 53 * @return int 54 */ 55 function getStatus() { 56 return $this->val; 57 } 58} 59 60/** 61 * and observer class 62 */ 63class Observator implements SplObserver { 64 function update(SplSubject $subiect) { 65 echo $subiect->getStatus(); 66 } 67} 68 69// an observer instance 70$observator = new Observator(); 71 72// an subject instance 73$subiect = new Actiune(); 74 75// attaching an observer to the subject 76$subiect->attach($observator); 77 78// update subject 79$subiect->update(5);What seems strange is that there isn’t any documentation on this SPL interfaces. Even on the Zend website there is an article PHP Patterns: The Observer Pattern which does not use SPL, but for something like namespaces there was documentation even before PHP 5.3 was out.